Year
2021Abstract
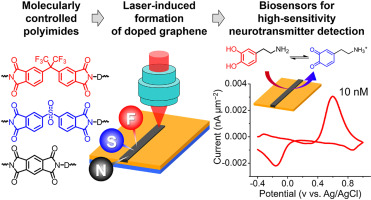
Fabrication of heteroatom-doped graphene electrodes remains a challenging endeavor, especially on flexible substrates. Precise chemical and morphological control is even more challenging for patterned microelectrodes. We herein demonstrate a scalable process for directly generating micropatterns of heteroatom-doped porous graphene on polyimide with different backbones using a continuous-wave infrared laser. Conventional two-step polycondensation of 4,4′-oxydianiline with three different tetracarboxylic dianhydrides enabled the fabrication of fully aromatic polyimides with various internal linkages such as phenylene, trifluoromethyl or sulfone groups. Accordingly, we leverage this laser-induced polymer-to-doped-graphene conversion for fabricating electrically conductive microelectrodes with efficient utilization of heteroatoms (N-doped, F-doped, and S-doped). Tuning laser fluence enabled achieving electrical resistivity lower than ∼13 Ω sq–1 for F-doped and N-doped graphene. Finally, our microelectrodes exhibit superior performance for electrochemical sensing of dopamine, one of the important neurotransmitters in the brain. Compared with carbon fiber microelectrodes, the gold standard in electrochemical dopamine sensing, our F-doped high surface area graphene microelectrodes demonstrated 3 order of magnitude higher sensitivity per unit area, detecting dopamine concentrations as low as 10 nM with excellent reproducibility. Hence, our approach is promising for facile fabrication of microelectrodes with superior capabilities for various electrochemical and sensing applications including early diagnosis of neurological disorders.